Getting Started
Equation Display
The equation display shows all of the operations you have entered since the last time Clear All (
You can scroll up or down and make changes to any line. Any changes will be reflected instantly in the calculations.
If the line you want to change is not already highlighted, scroll to the desired line and select it by tapping it one time. Once the line has been selected you have the following options:
- Change the value on the line by entering a new number
- Change the operator on the line by entering a new operator
- Change by the value and the operator
- Clear the line and enter a new operation
- Activate the In-Line Menu (see Advanced Topics)
Shift Functions
Shift Functions are printed above the keys. 

Date Math
Dates are recognized by use of the 
Results
OmniCalc® can display up to 16 digits plus a minus sign and a 2 digit exponent. Results with more than 16 digits will display in scientific notation.
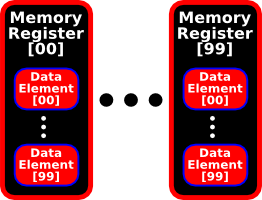
Memory
OmniCalc® has a 100 by 100 memory matrix. The figure below shows the layout of OmniCalc®‘s 100 Memory Registers.
Each Memory Register has the capacity to hold 100 Data Elements. Advanced Statistical Operations explains more about accessing Data Tables. Additional operations that access Memory are described in Basic Memory Operations, Advanced Memory Operations and Basic Statistical Operations
Clear and Clear All

Clear the line at the current cursor location

Erase all lines
Note:
Hold 
Hold 
Equals

The 
If the cursor is located above an 



Parenthetical Expressions


Parenthetical expressions can be nested to a depth of 100 levels within 

Pressing 

Simple Operations
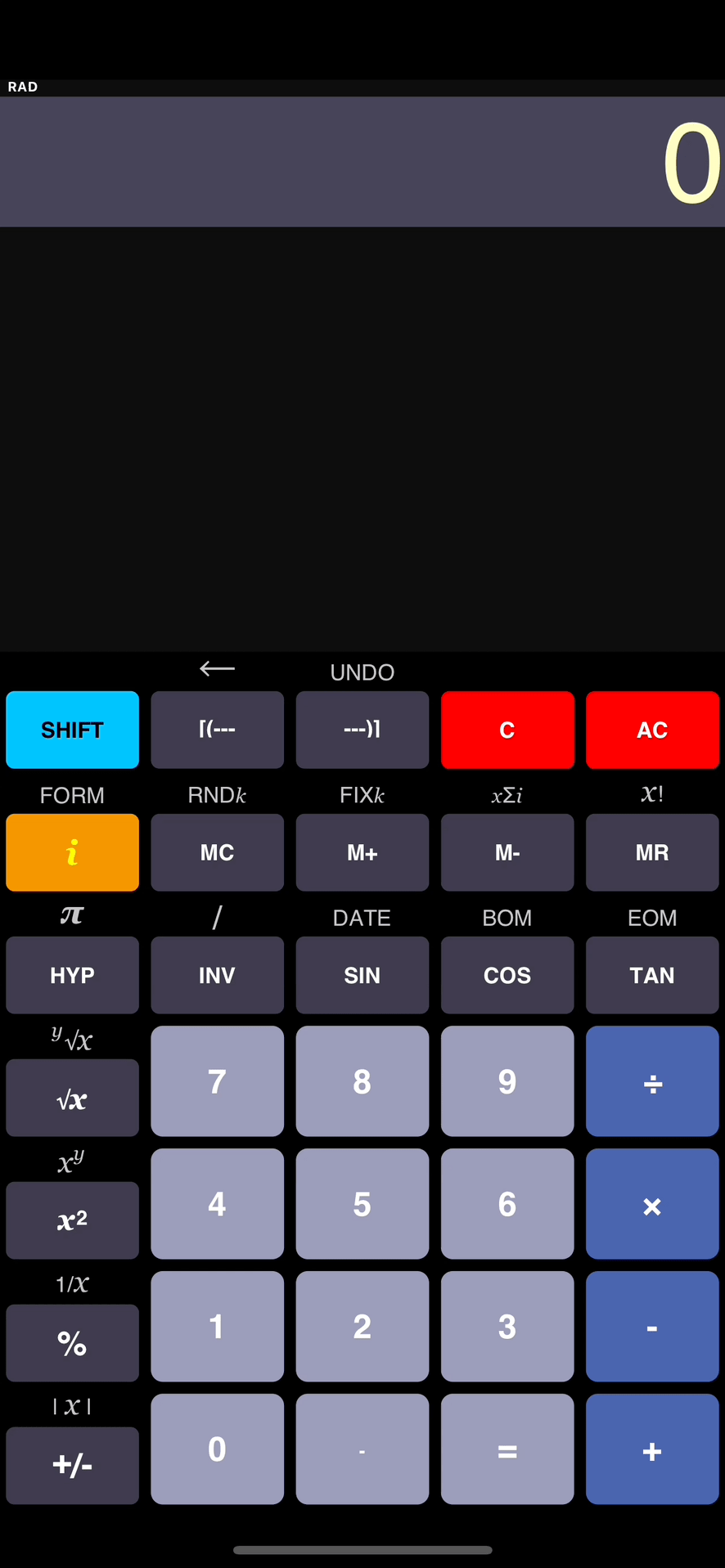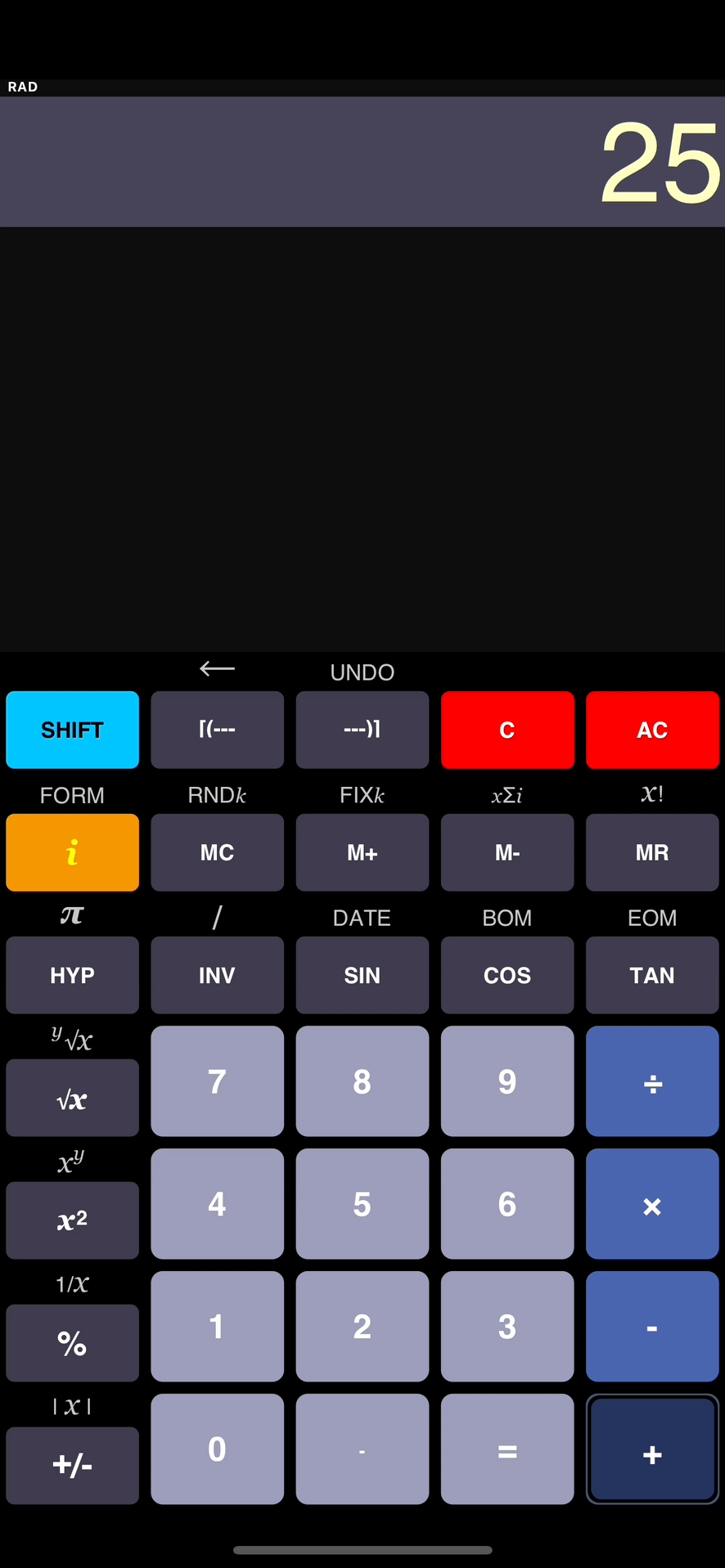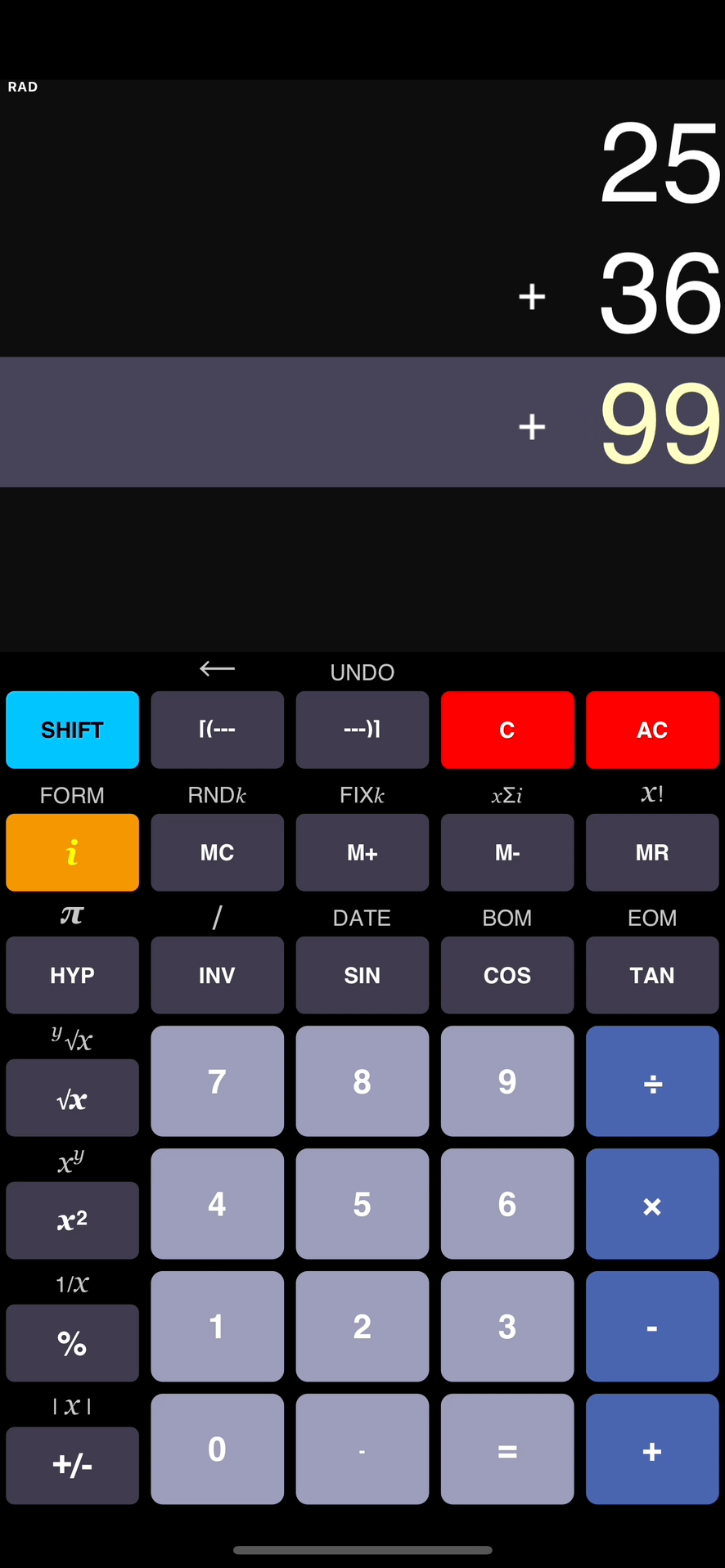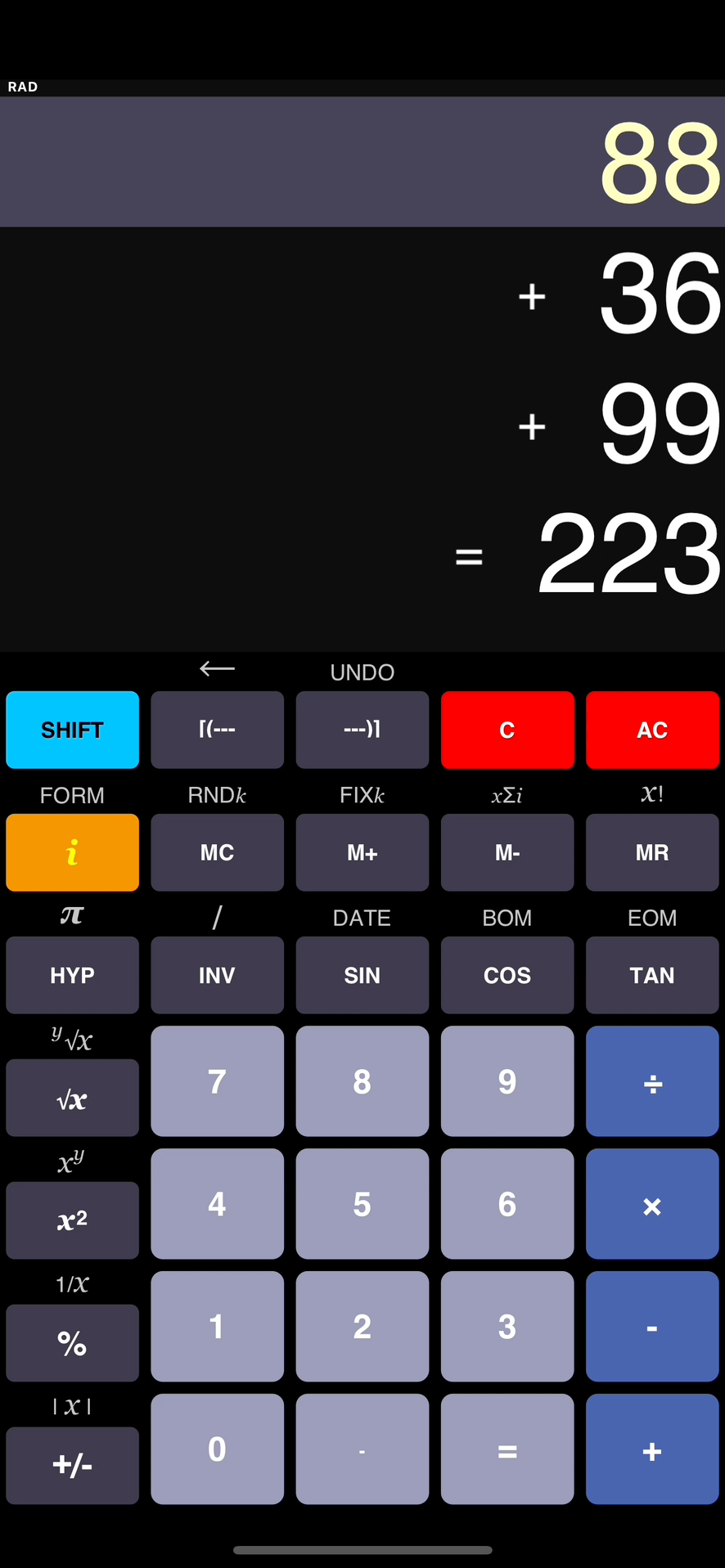
Addition
- 1
1
2
Subtraction
- 10
2
8
Multiplication
- 5
6
30
Division
- 35
7
5
Negation
- 15
6
-9
Absolute value
- -5
6
11
Reciprocal
- 5
100
20
Fix to k
- 5.12853
2
5.12
Round to k
- 5.12853
2
5.13
Basic Memory Operations
Basic Memory Operations use Data Element [00] of Memory Register [00]
Add to Memory
- 25
Subtract from Memory
- 5
Recall from Memory
20
Clear Memory
Advanced Memory Operations
Advanced Memory Operations use Data Element [00] from any of the referenced Memory Registers [00] through [99]
Put in Memory Register [##]
- 45
[12]
Add to Memory Register [##]
- 25
[12]
Subtract from Memory Register [##]
- 5
[12]
Recall from Memory Register [##]
[12]
65
Notes: Clear Memory: Holding 
Clear Form: Holding 
Date Operations
- Add Days
- 1/1
12
01/13/2010
- 5
12/16
12/21/2010
- Subtract Days
- 5/2
10
04/22/2010
- Subtract Dates
- 5/2
4/3
29
Percent Operations
- Percentage (10% of 1000)
- 1000
10
100
- Ratio (Ratio of 30 to 6)
- 30
6
500
- Increase (Add 18% to $25.00)
- 25
18
29.50
- Discount (Marked down 9% from $100.00)
- 100
9
91
Constants

The PI constant is calculated internally as 3.14159265358979323846264338327

Generates a random value between 0 and 232

Inserts the current date in the format MM/DD/YYYY

Inserts the first day of the current month in the format MM/DD/YYYY

Inserts the last day of the current month in the format MM/DD/YYYY
Integer Summation

- 232
27028
Integer Factorial

- 7
5040
Permutations
A permutation is an arrangement of objects in which order is important.

An example would be to calculate the number of possible outcomes for the first, second and third place positions of a horse race if there are 8 horses in the running.
Number of Permutations
- 8
3
336
Combinations
A combination is an arrangement of objects in which order is not important.

An example would be to calculate how many different combinations of 5 cards each can be dealt from a deck of 52 cards.
Number of Combinations
- 52
5
2598960
Exponentiation
Squared
- 5
25
Square Root
- 36
6
Power of Y
- 9
3
729
Root of Y
- 16
4
2
Logarithmic Functions
Logarithm
- 100
2
10x
- 2
100
Natural Logarithm
- 5
1.609437912434
Exponential Function
- 1.609437912434
5
e constant is calculated as 2.7182818284590451
Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric Functions will be based on angular units represented in Degrees, Radians or Gradians. You can change the angle units for all Trigonometric Functions in the OmniCalc® Controls. The default setting is Radians.
Sine
0
Cosine
1
Tangent
- 1
1.557407724655
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Inverse Trigonometric Functions will either have a direct access button as shown below or they will be accessed by pressing the 
The symbol INV will appear at the top of the Equation Display to indicate when Trigonometric Functions (




Inverse Sine
Inverse Cosine
Inverse Tangent
Hyperbolic Functions
Hyperbolic Functions will either have a direct access button as shown below or they will be accessed by pressing the 
The symbol HYP will appear at the top of the Equation Display to indicate when Trigonometric Functions (




Hyperbolic Sine
Hyperbolic Cosine
Hyperbolic Tangent
Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
Inverse Hyperbolic Functions will either have a direct access button as shown below or they will be accessed by pressing the 

The symbols HYP/INV will appear at the top of the Equation Display to indicate when Trigonometric Functions (




Inverse Hyperbolic Sine
Inverse Hyperbolic Cosine
Inverse Hyperbolic Tangent
Basic Statistical Operations
Basic Statistical Operations use Data Elements [00] through [99] from Memory Register [00]
Insert Data Element
- 15
25
19
12
Delete Data Element
- 25
Number of Data Elements
3
Average of Data Elements
15.3333
Minimum Data Element
12
Maximum Data Element
19
Sum of Data Elements
46
Sample Standard Deviation
3.511884584284
Population Standard Deviation
2.867441755681
Advanced Statistical Operations
Advanced Statistical Operations use Data Elements [00] through [99] from any of the referenced Memory Registers [00] through [99]
Insert Data Element to Register [##]
- 15
[12]
25
[12]
19
[12]
12
[12]
Delete Data Element From Register [##]
- 25
[12]
Number of Data Elements in Register [##]
[12]
3
Average of Data Elements in Register [##]
[12]
15.3333
Minimum Data Element in Register [##]
[12]
12
Maximum Data Element in Register [##]
[12]
19
Sum of Data Elements in Register [##]
[12]
46
Sample Standard Deviation from Register [##]
[12]
3.511884584284
Population Standard Deviation from Register [##]
[12]
2.867441755681
Controls
The OmniCalc® controls is where you can change the style and certain behaviors of your calculator.
Advanced Topics
In-Line Menu
Slide your finger across any non-blank line in the equation display to activate the In-Line Menu.
The In-Line Menu gives you the following options:
INSERT – insert a new line into the equation
DELETE – delete the selected line
LABEL – label the selected line
CANCEL – clear the menu without making changes

 Addition
Addition Subtraction
Subtraction Multiplication
Multiplication Division
Division Negation
Negation Absolute value
Absolute value Reciprocal
Reciprocal Fix to k
Fix to k Round to k
Round to k Add to Memory
Add to Memory Subtract from Memory
Subtract from Memory Recall from Memory
Recall from Memory Clear Memory
Clear Memory Put in Memory Register [##]
Put in Memory Register [##] Add to Memory Register [##]
Add to Memory Register [##] Subtract from Memory Register [##]
Subtract from Memory Register [##] Recall from Memory Register [##]
Recall from Memory Register [##]
 Squared
Squared Square Root
Square Root Power of Y
Power of Y Root of Y
Root of Y Logarithm
Logarithm 10x
10x Natural Logarithm
Natural Logarithm Exponential Function
Exponential Function Inverse Sine
Inverse Sine Inverse Cosine
Inverse Cosine Inverse Tangent
Inverse Tangent Hyperbolic Sine
Hyperbolic Sine Hyperbolic Cosine
Hyperbolic Cosine Hyperbolic Tangent
Hyperbolic Tangent Inverse Hyperbolic Sine
Inverse Hyperbolic Sine Inverse Hyperbolic Cosine
Inverse Hyperbolic Cosine Inverse Hyperbolic Tangent
Inverse Hyperbolic Tangent Insert Data Element
Insert Data Element Delete Data Element
Delete Data Element Number of Data Elements
Number of Data Elements Average of Data Elements
Average of Data Elements Minimum Data Element
Minimum Data Element Maximum Data Element
Maximum Data Element Sum of Data Elements
Sum of Data Elements Sample Standard Deviation
Sample Standard Deviation Population Standard Deviation
Population Standard Deviation Delete Data Element From Register [##]
Delete Data Element From Register [##] Number of Data Elements in Register [##]
Number of Data Elements in Register [##] Average of Data Elements in Register [##]
Average of Data Elements in Register [##] Sum of Data Elements in Register [##]
Sum of Data Elements in Register [##] Sample Standard Deviation from Register [##]
Sample Standard Deviation from Register [##] Population Standard Deviation from Register [##]
Population Standard Deviation from Register [##]